Interventional Cardiology
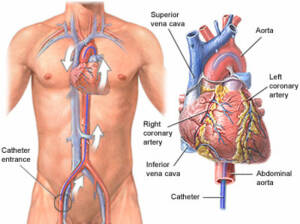
Cardiac Catherization
Cardiac catheterization is a widely used procedure to diagnose and treat various heart conditions effectively. During this minimally invasive procedure, a thin, flexible tube called a catheter is carefully inserted through a blood vessel in the arm, leg, or neck and advanced to the heart. This procedure enables healthcare providers to perform crucial diagnostic tests and interventions.
Key Aspects of Cardiac Catheterization:
- Diagnostic Precision: Cardiac catheterization allows for precise measurements of blood pressure in the heart chambers, assessment of blood flow across heart valves, and identification of coronary artery blockages.
- Minimally Invasive: This procedure is minimally invasive, typically resulting in shorter recovery times and reduced risks.
- Customized Care: Cardiac catheterization is tailored to address specific heart conditions, offering an individualized approach to treatment.
- Quick Recovery: Most patients can return home the same day, with some cases requiring an overnight hospital stay.
Coronary Artery Disease
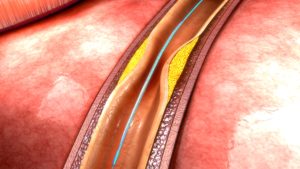
The intricate process of arterial blockages and the development of angina is a complex but crucial aspect of heart health. Elevated cholesterol levels, inflammation, and vascular injuries can contribute to the accumulation of fat and cholesterol within the heart’s arteries, often occurring asymptomatically for years. As these atheromas grow, the arteries adapt by dilating until they reach their limit, leading to the term “stenosis.”
Key Aspects:
- Asymptomatic Progression: Blockages can develop for many years without causing noticeable symptoms, highlighting the importance of regular heart health assessments.
- Angina Symptoms: Angina manifests as chest pain or pressure, shortness of breath, and fatigue during exertion or stress, signifying compromised blood flow to the heart.
- Management: Medications may be employed to improve blood flow, but when they prove insufficient, catheterization becomes essential to identify blockages.
- Intervention: Angioplasty, involving balloon dilation of an artery, and stenting, the insertion of a metal scaffold to maintain artery openness, can effectively address blockages.
Heart Attack/Myocardial Infarction
The progression of Coronary Artery Disease typically follows a continuous course, but certain conditions, such as stress, illness, or increased cardiac workload, can accelerate this process. Under such circumstances, angina may not manifest predictably but can occur suddenly, even during sleep. This abrupt reduction in blood flow to the heart, often caused by a ruptured cholesterol plaque, a blood clot, or rapid stenosis deterioration, is termed a Myocardial Infarction, or Heart Attack.
Key Aspects:
- Heart Attack: A Myocardial Infarction results from the sudden, severe deprivation of blood and oxygen to a portion of the heart muscle, leading to damage detectable through EKG and blood testing.
- Risks and Complications: Heart Attack survivors face risks like weakened heart muscles, dangerous heart rhythm irregularities, recurring chest pain, and further Heart Attacks.
- Medical Intervention: Cardiac Catheterization, in combination with blood-thinning medications, can restore blood flow to damaged heart areas while safeguarding healthy regions.
- Stent Utilization: Stents are often employed to prevent Restenosis, the recurrence of artery blockage, effectively reducing the likelihood of repeat events and potentially extending a patient’s life.
Heart Failure
The heart’s primary function is to serve as a pump, supplying blood and oxygen to the body’s organs and tissues. However, in cases of Heart Failure, the heart’s efficiency is compromised, leading to inadequate oxygen delivery. Heart Failure can manifest with various symptoms, including shortness of breath, fatigue, swelling, nausea, bloating, coughing, weight gain, and abdominal discomfort. While Heart Failure is often attributed to a weakened heart muscle, approximately half of cases result from the heart’s inability to relax effectively, even while maintaining normal contractions.
Several factors can contribute to Heart Failure, such as arterial blockages, inflammatory conditions, rhythm disturbances, high blood pressure, kidney disease, and various other ailments. To pinpoint the exact cause of Heart Failure, a comprehensive heart catheterization is performed, which entails measuring pressures within all heart chambers and assessing oxygen levels through multiple blood samples.
Key Aspects:
- Heart Failure Symptoms: Shortness of breath, fatigue, swelling, nausea, bloating, coughing, weight gain, and abdominal discomfort.
- Underlying Causes: Heart Failure can result from a weakened heart muscle or an inability of the heart to relax properly, often triggered by diverse factors.
- Diagnostic Precision: A heart catheterization procedure provides invaluable insights into heart chamber pressures and blood oxygen levels, facilitating tailored medical therapy for each patient’s unique Heart Failure cause.
Heart Valve Disease
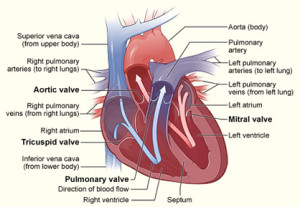
The heart, with its four chambers and valves, plays a crucial role in maintaining blood circulation by preventing backward flow during each heartbeat. These remarkable valves, thin as paper, tirelessly open and close between 60 to 100 times per minute throughout one’s lifetime. However, due to factors like prolonged use, high blood pressure, inflammation, and various other reasons, heart valves can deteriorate over the years. Some valves may become stenotic, too tight to function properly, while others may develop regurgitation, causing leakage and disrupting normal blood flow. These valve problems can lead to a range of health issues, including heart failure, coughing, shortness of breath, rhythm disturbances, fainting, and, in severe cases, mortality.
At Heart & Health Medical, we employ noninvasive tests such as Echocardiograms and EKGs to begin the diagnosis of valve diseases. In many instances, diagnosing valve problems with greater precision necessitates measuring pressure and flow directly across the valves through a cardiac catheterization procedure. Fortunately, many valve issues can now be effectively treated through minimally invasive procedures, offering patients comprehensive treatment without the risks associated with open-heart surgery. Procedures like TAVR (Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement), MitraClip, and Valvuloplasty, among the most advanced in medicine, are performed with safety and ease in a Cardiac Catheterization Lab.
Key Aspects:
- Heart Valve Function: Four heart chambers and valves maintain blood flow and prevent backflow during each heartbeat.
- Valve Damage: Valves can degrade over time, becoming stenotic (too tight) or regurgitant (leaky), leading to various health issues.
- Diagnosis: Noninvasive tests, such as Echocardiograms and EKGs, initiate the diagnosis of valve diseases.
- Precise Diagnosis: Cardiac catheterization measures pressure and flow across valves, allowing for accurate diagnosis.
- Minimally Invasive Treatment: Advanced procedures like TAVR, MitraClip, and Valvuloplasty offer comprehensive valve disease treatment with enhanced safety.
Pulmonary Hypertension
Throughout your life, your heart and lungs collaborate to deliver oxygen to your body while eliminating waste products, particularly carbon dioxide. In the same way your doctor assesses blood pressure in your body, the pressure within the arteries of the lungs can be measured using delicate catheters. Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) is characterized by elevated pressure in the pulmonary arteries, which can result from various factors such as heart failure, valve disease, lung diseases, chronic infections, congenital heart disease, and arterial disorders.
Through the catheterization procedure, healthcare professionals can directly measure the pressure in the pulmonary arteries and employ different medications to pinpoint the precise cause of elevated pressures. This diagnostic approach enables doctors to provide a more accurate diagnosis, leading to a tailored medication regimen that addresses the specific underlying cause of Pulmonary Hypertension.
At Heart & Health Medical, we are dedicated to providing comprehensive diagnosis and treatment for Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension, ensuring each patient receives personalized care to manage their condition effectively.

