Heel Pain: Identifying the Culprit and Finding Relief If you’ve...
Read More
Best Podiatrist Long Island
Long Island's Top-Rated Podiatry
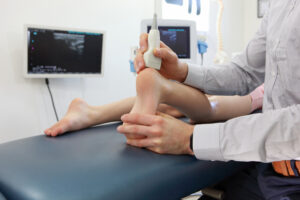
At Heart and Health Medical, we are dedicated to providing comprehensive podiatry care to patients across Long Island, New York. With four convenient locations in Plainview, North Babylon, Coram, and Massapequa, our experienced and board-certified podiatrist, along with our knowledgeable staff, are committed to delivering top-quality foot and ankle healthcare.
Comprehensive Podiatry Care at Heart and Health Medical
At Heart and Health Medical we are dedicated to providing comprehensive podiatry care to patients across Long Island, New York. With four convenient locations in Plainview, North Babylon, Coram, and Massapequa, our experienced and board-certified podiatrist, along with our knowledgeable staff, are committed to delivering top-quality foot and ankle healthcare.
Why Choose Heart and Health Medical for Podiatry Care?
- Board-Certified Podiatrist: Our podiatrist is board-certified and highly experienced in diagnosing and treating a wide range of foot and ankle conditions.
- Advanced Technology: We utilize the latest diagnostic tools and technology to provide accurate assessments and effective treatments.
- Personalized Care: Each patient receives individualized care and treatment plans tailored to their unique needs and goals.
- Comprehensive Approach: Our podiatrist works closely with other medical specialists within our practice, ensuring seamless coordination of care for patients with multiple health concerns.
- Convenient Locations: With four convenient locations on Long Island, you can easily access our podiatry services near you.
- Patient-Centered Care: Your comfort, well-being, and satisfaction are our top priorities. We take the time to listen to your concerns and answer your questions.
If you’re experiencing foot or ankle pain, discomfort, or have any concerns about your lower extremities, don’t hesitate to reach out to Heart and Health Medical, PLLC. Our expert podiatrist and dedicated staff are here to help you maintain healthy, pain-free feet and ankles. Contact us today to schedule an appointment or learn more about our podiatry services.
Podiatry Expert
Long Island's Best Podiatrist

Podiatrist Near Me
What is Podiatry?
Podiatry is a specialized branch of medicine focused on the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of disorders and conditions affecting the feet, ankles, and lower extremities. Podiatrists, also known as doctors of podiatric medicine (DPMs), undergo extensive training to become experts in this field. They are equipped to address a wide range of foot and ankle issues, from common conditions to more complex problems.
Our Podiatry Services
At Heart and Health Medical, we offer a comprehensive range of podiatry services, including:
- Foot and Ankle Examinations: Our podiatrist conducts thorough examinations to assess your foot and ankle health, identify any issues, and develop personalized treatment plans.
- Foot and Ankle Pain Management: We provide effective pain management solutions for various conditions, including arthritis, plantar fasciitis, Achilles tendonitis, and more.
- Ingrown Toenail Treatment: Our podiatrist offers expert care for ingrown toenails, relieving pain and preventing complications.
- Diabetic Foot Care: We specialize in diabetic foot care to help prevent and manage foot complications associated with diabetes.
- Sports Injury Treatment: If you’ve experienced a sports-related foot or ankle injury, we can provide prompt evaluation and treatment to get you back on your feet.
- Orthotics: Custom orthotic devices can be prescribed to address issues related to gait, arch support, and foot comfort.
- Foot and Ankle Surgery: When necessary, our podiatrist is skilled in performing surgical procedures to address a wide range of foot and ankle conditions.
- Bunion and Hammertoe Treatment: We offer both conservative and surgical treatment options for bunions and hammertoes.
- Wound Care: Comprehensive wound care is available for foot ulcers, non-healing wounds, and other related conditions.
- Fungal Nail Treatment: Our podiatrist can provide effective solutions for fungal nail infections.
- Foot and Ankle Trauma: Whether you’ve experienced a fracture, sprain, or trauma to the foot or ankle, we offer timely and expert care.
- Custom Footwear Guidance: We can recommend appropriate footwear to support your foot health and address specific conditions.
Podiatry Articles
Orthotics and Their Role in Foot Health
Orthotics and Their Role in Foot Health The foundation of...
Read MoreSports Podiatry: Keeping Athletes on Their Feet
Sports Podiatry: Keeping Athletes on Their Feet Introduction to Sports...
Read MoreFoot Care Specialist
Achilles Tendon Rupture
The Achilles tendon is a robust fibrous band of tissue that connects the calf muscles (the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles) to the heel bone (the calcaneus). It plays a crucial role in various movements of the foot and ankle, such as pointing the foot downward (plantarflexion), which is essential for walking, running, and jumping. However, the Achilles tendon is susceptible to injury, and one of the most severe injuries it can sustain is a rupture.
Causes of Achilles Tendon Rupture: Achilles tendon ruptures typically occur when the tendon is subjected to excessive force or stress beyond its capacity. Common causes and risk factors for Achilles tendon rupture include:
Sudden Forceful Movement: A sudden, forceful push-off with the foot or a rapid change in direction, especially during sports activities, can overload the Achilles tendon and lead to a rupture.
Aging: As people age, the Achilles tendon may weaken and become more prone to injury.
Tight Calf Muscles: Having tight or inflexible calf muscles can increase the risk of Achilles tendon rupture.
Previous Tendon Injuries: A history of Achilles tendon injuries or inflammation can weaken the tendon and make it more susceptible to rupture.
Symptoms of Achilles Tendon Rupture: An Achilles tendon rupture can cause sudden and severe symptoms, including:
Pain: Often described as a sharp or stabbing pain in the back of the ankle or calf.
Swelling: Swelling may occur around the affected area.
Difficulty Walking: Patients may have difficulty walking or bear weight on the injured leg.
Weakness: A noticeable decrease in strength when attempting to push off with the foot.
Ankle Deformity: In some cases, an obvious indentation or deformity at the back of the ankle may be visible.
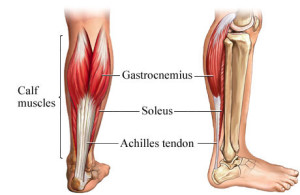
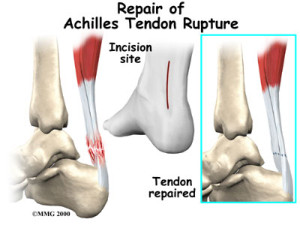
Achilles Tendon Rupture Treatment
Treatment of Achilles Tendon Rupture: The treatment approach for an Achilles tendon rupture may vary depending on the severity of the injury, the patient’s age, activity level, and overall health. Common treatment options include:
Non-Surgical Treatment: This approach may involve wearing a cast or walking boot with the ankle positioned in a specific way to promote healing. Physical therapy is often a part of non-surgical treatment.
Surgical Repair: Surgery may be recommended for younger, more active individuals or in cases of complete tendon tears. Surgical repair involves stitching the torn ends of the tendon back together.
Rehabilitation: Regardless of the treatment chosen, rehabilitation is a crucial aspect of recovery. Physical therapy and exercises are essential for restoring strength, flexibility, and function to the injured leg.
It’s essential to seek prompt medical attention if you suspect an Achilles tendon rupture. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can help prevent complications and promote a successful recovery.
Ankle Sprain
nkle sprains are common injuries that occur when the ligaments in or around the ankle are stretched, torn, or damaged. Ligaments are tough bands of fibrous tissue that connect bones to one another, and they play a crucial role in providing stability to the ankle joint during various movements. Ankle sprains can result from a variety of causes, and they are characterized by symptoms such as pain, swelling, bruising, and difficulty walking. There are different types of ankle sprains, categorized based on the severity of the injury.
Causes of Ankle Sprains: The most common causes of ankle sprains include:
Trauma: Ankle sprains often occur due to traumatic incidents, such as:
- Falls: A sudden fall, especially from a height or while participating in sports, can lead to an ankle sprain.
- Twisting: Sudden twisting or rolling of the ankle while walking or running can strain or tear the ligaments.
- Impact: A direct blow to the ankle joint can cause ligament injury.
Sports Injuries: Participation in sports activities that involve jumping, running, and quick changes in direction increases the risk of ankle sprains. Sports like basketball, soccer, and volleyball are common culprits.
Uneven Surfaces: Walking or running on uneven terrain or surfaces can lead to loss of balance and ankle sprains.
Symptoms of Ankle Sprains: Ankle sprains can produce a range of symptoms, which may include:
- Pain: An immediate or delayed onset of pain at the site of the injury.
- Swelling: Swelling around the ankle joint, which can be mild to severe.
- Bruising: Skin discoloration or bruising may develop due to bleeding into the tissues.
- Difficulty Walking: Pain and instability can make it challenging to bear weight on the affected ankle.
- Stiffness: Reduced range of motion and stiffness in the ankle joint.
Types of Ankle Sprains: Ankle sprains are typically classified into three grades based on the severity of ligament damage:
Grade I (Mild): In a Grade I sprain, the ligaments are stretched but not torn. Pain and swelling are typically mild, and there is minimal to no joint instability.
Grade II (Moderate): Grade II sprains involve partial tearing of the ligaments. These injuries result in more significant pain, swelling, and mild to moderate joint instability.
Grade III (Severe): Grade III sprains are characterized by complete ligament tears. These injuries cause severe pain, swelling, joint instability, and often require more extensive treatment.
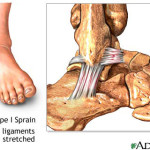
The first is less serious and occurs when the ligament is over stretched.
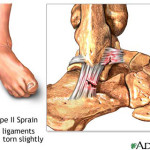
The second type of sprain is when the ligaments become slightly torn.
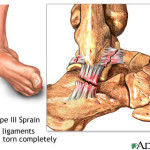
The third type of sprain is the most serious and occurs when the ligament is completely torn.
Ankle Sprain Treatment
Treatment of Ankle Sprains: The treatment approach for ankle sprains depends on the severity of the injury but may include:
Rest: Resting the injured ankle and avoiding putting weight on it is crucial in the early stages of healing.
Ice: Applying ice to the injured area can help reduce swelling and pain.
Compression: Wrapping the ankle with an elastic bandage can provide support and minimize swelling.
Elevation: Keeping the ankle elevated above heart level can help reduce swelling.
Pain Medication: Over-the-counter pain relievers may be recommended to manage pain and inflammation.
Physical Therapy: Rehabilitation exercises can help improve strength, flexibility, and stability in the ankle.
Bracing or Taping: Depending on the severity of the sprain, a brace or tape may be used to support the ankle during recovery.
For severe ankle sprains, or Grade III injuries, surgical intervention may be necessary to repair torn ligaments.
Athletes Foot
Athlete’s foot, also known as tinea pedis, is a common fungal infection that primarily affects the feet. It is caused by various types of fungi, such as Trichophyton or Epidermophyton, and typically thrives in warm, moist environments, making the feet an ideal location for its growth. Athlete’s foot can be highly contagious and is often contracted in places like public showers, swimming pools, and locker rooms. Here’s an overview of athlete’s foot, its symptoms, and treatment:
Causes of Athlete’s Foot: Athlete’s foot is caused by exposure to fungi, particularly in conditions that promote fungal growth, including:
Warm and Moist Environments: Fungi responsible for athlete’s foot flourish in warm, humid, and damp conditions, such as sweaty shoes and socks.
Direct Contact: The fungus can spread through direct contact with an infected person’s feet or by touching contaminated surfaces in public areas.
Shared Items: Sharing shoes, socks, towels, or personal items with an infected person can increase the risk of contracting athlete’s foot.
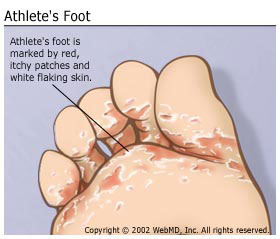
Symptoms of Athlete’s Foot: Athlete’s foot typically presents with several characteristic symptoms, including:
Itching: Persistent itching, often intense, on the affected areas of the foot, particularly between the toes.
Burning Sensation: A burning or stinging sensation in the affected areas.
Redness and Scaling: Skin on the feet, especially between the toes, may become red, scaly, and dry.
Blisters: Small, fluid-filled blisters may develop, leading to oozing and crusting.
Cracked Skin: Skin may become cracked and painful, potentially leading to open sores.
Discolored Nails: In some cases, the fungus can spread to the toenails, causing discoloration, thickening, and crumbled nails.
Treatment of Athlete’s Foot: Athlete’s foot is usually a treatable condition with various over-the-counter antifungal medications. Treatment options include:
Topical Antifungal Creams: Applying antifungal creams or ointments directly to the affected areas can effectively eliminate the fungus. Common active ingredients include clotrimazole, terbinafine, miconazole, or tolnaftate.
Powders or Sprays: Antifungal powders or sprays can help keep the feet dry and prevent fungal growth.
Oral Medications: In severe cases or when topical treatments are ineffective, a healthcare provider may prescribe oral antifungal medications.
Good Foot Hygiene: Practicing good foot hygiene, such as keeping the feet clean and dry, changing socks daily, and wearing well-ventilated shoes, can help prevent the recurrence of athlete’s foot.
Avoiding Contaminated Areas: Reducing exposure to sources of infection, such as avoiding walking barefoot in public showers or locker rooms, can help prevent athlete’s foot.
It’s essential to follow the recommended treatment regimen and continue treatment for the prescribed duration, even if symptoms improve, to ensure complete eradication of the fungus and prevent recurrence.
If symptoms persist, worsen, or spread, or if there is a secondary bacterial infection, it’s advisable to consult a healthcare provider for a more comprehensive evaluation and treatment plan. Additionally, individuals with diabetes or compromised immune systems should seek prompt medical attention for any foot infection.
Brachymetatarsia
Brachymetatarsia is a medical condition characterized by the abnormally short length of one or more metatarsal bones in the foot, most commonly affecting the fourth toe. This condition arises due to the premature closure of the growth plate in the affected bone, preventing it from reaching its full developmental length. While brachymetatarsia may seem like a minor issue, it can disrupt the normal physiology of the foot, particularly the distribution of weight during walking. Here is an overview of brachymetatarsia, its causes, symptoms, and potential treatment options:
Causes of Brachymetatarsia: The primary cause of brachymetatarsia is the early closure of the growth plate in one or more metatarsal bones. This premature closure hinders the bone’s ability to continue growing, resulting in a shorter metatarsal relative to the others. The reasons for this early closure can vary but are often idiopathic, meaning they occur without a known cause. However, some potential contributing factors include genetics and hereditary factors.
Symptoms of Brachymetatarsia: Brachymetatarsia may not always cause noticeable symptoms, especially in mild cases. However, individuals with this condition may experience the following:
Shortened Toe: The affected toe, typically the fourth, is noticeably shorter than the adjacent toes.
Cosmetic Concerns: Many people with brachymetatarsia seek medical attention due to cosmetic concerns or self-esteem issues related to the appearance of the affected toe.
Discomfort: In some cases, individuals may experience discomfort or pain in the affected toe, especially when wearing certain shoes.
Treatment for Brachymetatarsia: The treatment of brachymetatarsia depends on the severity of the condition and the associated symptoms. Treatment options include:
Orthotic Devices: Custom-made shoe inserts or orthotics can help redistribute weight and reduce pressure on the affected toe. These devices can improve comfort and alleviate discomfort.
Shoe Modifications: Wearing shoes with extra padding or a wider toe box can help accommodate the shorter toe and reduce friction and discomfort.
Cosmetic Surgery: In cases where the cosmetic appearance of the affected toe is a significant concern, some individuals may opt for cosmetic surgical procedures. This typically involves lengthening the shortened metatarsal bone using techniques like bone grafts or gradual distraction osteogenesis. However, these procedures are usually elective and not performed solely for functional improvement.
Monitoring: In milder cases of brachymetatarsia with minimal symptoms, regular monitoring by a healthcare provider may be sufficient to ensure there are no significant functional issues or complications.
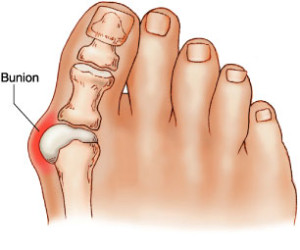
What are Bunions?
A bunion is a bump on the inner side of the foot, right by the big toe. These occur overtime when the big toe begins to shift inward to the second toe. This shift is what causes the big bump on the side of the foot and usually causes inflammation of the tissue in between the tendon and muscle of the toe. Bunions are caused by genetic factors but are not genetically passed down. In addition, foot traumas, arthritis, and improper shoewear may contribute to the formation of bunions.
Bunion Treatment
Treatment of bunions can be surgical or nonsurgical. Non surgical options include things such as padding for more support and anti-inflammatory drugs to help with the swelling. If the pain is extreme and no other non-surgical methods work, surgery can be an option. The goal of surgery is to remove the bump and repair the bone structures that have been changed due to the shifting of bones.
Calcaneal Apophysitis
Calcaneal apophysitis, also known as Sever’s disease, is a medical condition that primarily affects children between the ages of 8 and 14. It involves inflammation of the growth plate in the heel bone (calcaneus). This condition typically occurs during a child’s growth spurts when the heel bone is not yet fully developed. Here’s an overview of calcaneal apophysitis, including its causes, symptoms, and potential treatment options:
Causes of Calcaneal Apophysitis (Sever’s Disease): The primary cause of calcaneal apophysitis is repetitive stress and overuse of the heel’s growth plate. During growth spurts, the bones and tendons often grow at different rates, leading to increased tension and pressure on the growth plate in the heel. Several contributing factors can increase the risk of developing Sever’s disease, including:
Physical Activity: Children who participate in sports and activities that involve running, jumping, or sudden stops and starts are more susceptible to calcaneal apophysitis due to the repetitive impact on the heel bone.
Obesity: Excess body weight can increase the load and pressure on the heel, making obese children more prone to this condition.
Biomechanical Factors: Abnormal foot structures, such as flat feet (pes planus) or high arches (pes cavus), can affect the distribution of forces on the heel and contribute to Sever’s disease.
Tight Achilles Tendon: A tight Achilles tendon can put additional strain on the heel’s growth plate, increasing the risk of inflammation.
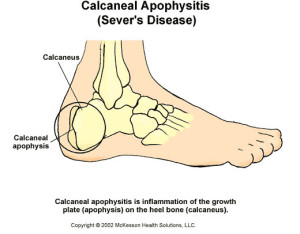
Symptoms of Calcaneal Apophysitis (Sever’s Disease): Children with Sever’s disease may experience various symptoms, including:
Heel Pain: Persistent pain in the heel, particularly during or after physical activities, is a hallmark symptom of Sever’s disease. The pain is usually located at the back of the heel or just beneath it.
Limping: The discomfort and pain may cause a child to limp or favor one foot while walking or running.
Tenderness: The affected heel may be tender to the touch.
Swelling: Some children may exhibit mild swelling around the affected heel area.
Treatment for Calcaneal Apophysitis (Sever’s Disease): The treatment of Sever’s disease focuses on relieving pain and reducing inflammation while allowing the heel to heal. Common treatment options include:
Rest: Reducing or temporarily discontinuing activities that place excessive stress on the heel can help promote healing. This may include avoiding or limiting participation in sports or high-impact activities.
Icing: Applying ice to the affected heel for 15-20 minutes several times a day can help reduce pain and inflammation.
Orthotic Inserts: Custom or over-the-counter shoe inserts (orthotics) can provide better arch support and cushioning, helping to distribute pressure more evenly across the foot.
Heel Cushions: Using heel cushions or cups in the shoes can help absorb shock and reduce pressure on the heel.
Stretching Exercises: Gentle stretching exercises for the calf muscles and Achilles tendon may be recommended to improve flexibility and reduce tension on the heel.
Anti-Inflammatory Medications: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may be prescribed to alleviate pain and inflammation.
Physical Therapy: In some cases, physical therapy may be recommended to address biomechanical issues and provide guidance on exercises and stretches.
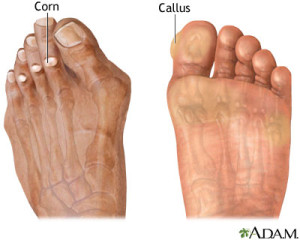
Corns and Calluses
Corns and callus are thickened layer of protective skin that results from consistent pressure and thickness. When the thickened skin forms on either the top or side of the toe it is referred to as a corn and when the thickened skin is on the bottom of your feet it is called a callus. This thickening of skin is actually a form of protection against blisters.
Corns and Callus Treatment
Corns and calluses are very minor conditions and usually go away overtime. The main way to get rid of these areas of thickened skin is to reduce the amount of friction in the feet. Proper fitted shoes and gloves can help prevent corns and callus.
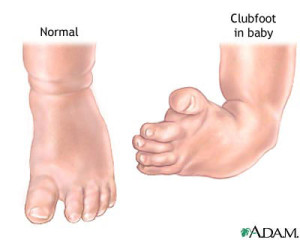
What is Charcot Foot (Clubfoot)?
Clubfoot is a medical deformity in which the foot points down and inward. This condition is present at birth and effects 1 in every 1,000. It generally is more common in males. There is no exact cause of clubfoot but it could possibly be genetic.
Clubfoot Treatment
The most common way to treat a clubfoot is to cast the foot. The sooner the cast is put on the better. Along with the cast, stretching techniques are required. This method is usually successful because a baby’s bones, ligaments, and tendons are all still flexible and easy to manipulate. An average baby will wear five to ten casts during their treatment, wearing each cast for about a week or two. The tenth cast will stay on for about 3 weeks. The baby will then need to wear a fulltime brace for about 3 months. After those 3 months, the brace should be worn only at night and when the baby naps. This last brace should be worn for 3 years. In most cases, the cause of the clubbed foot is a tight Achilles tendon. However, in half of the cases, the cast will not provide enough correction. If this is the case, surgery is needed to lengthen or shorten the ligaments and tendons.
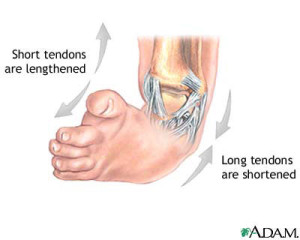
Facts about the Foot
- Each foot has 26 bones – both feet contain nearly one quarter of all the bones (206) on the body.
- Each foot is made up of an intricate network of over 100 tendons, ligaments, and muscles.
- Every step places 1.5 times your body weight of pressure on your foot (a 150-pound person places 225 pounds of pressure on the foot with every step).
- The average person walks 5,000 to 7,000 steps a day. The American Podiatric Medical Association (APMA) estimates that the average person will walk nearly 100,000 miles in a lifetime, between three to four times the Earth’s circumference.
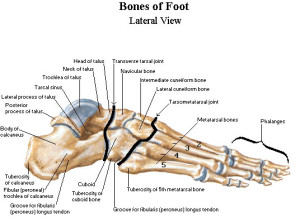
Other Services
- Compartment syndrome
- Diabetic Limb salvage
- Ganglion cyst
- Gangrene
- Gout
- Hammertoe
- Ingrown toenail
- Turf toe
- Ulcers
- Verrucae